What is Bearing Lock and How Does It Work in Mechanical Applications
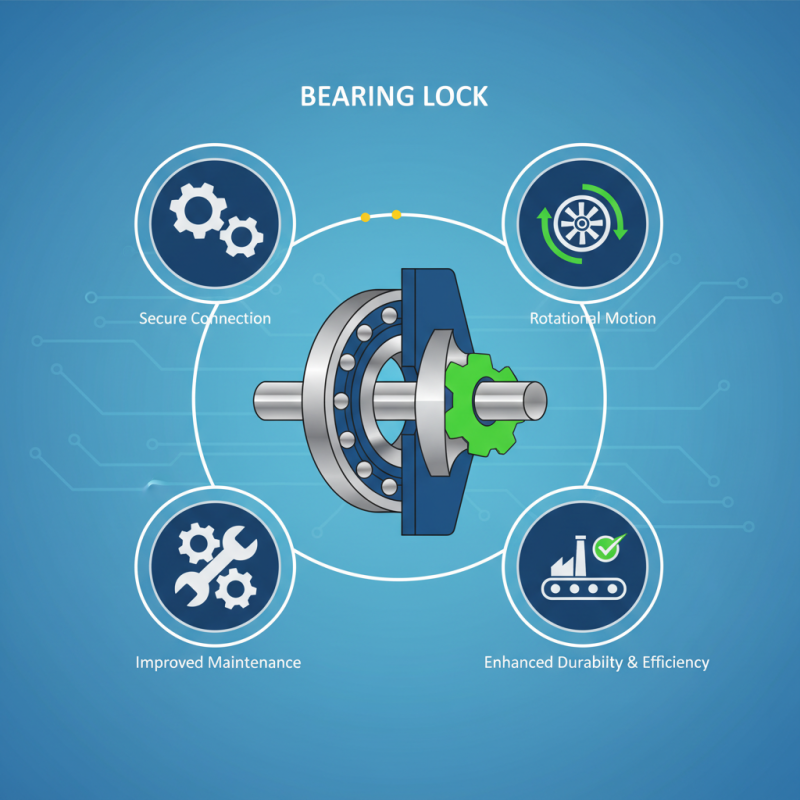
Bearing Lock is an essential concept in mechanical applications that plays a critical role in the performance and reliability of machinery. This innovative mechanism ensures that bearings are securely fixed in place, preventing any unintended movement that could lead to operational failures. By understanding how Bearing Lock functions, engineers and technicians can select the right solutions for their specific needs, ultimately enhancing the durability and efficiency of their systems.
The operation of Bearing Lock is fundamentally based on its ability to provide a secure connection while allowing for necessary rotational motion. This balance is vital in applications ranging from automotive to industrial machinery, where precision and stability are paramount. Through various methods and designs, Bearing Lock not only safeguards critical components but also improves maintenance practices, effectively minimizing downtime and associated costs.
In summary, the significance of Bearing Lock in mechanical applications cannot be overstated. Its role in ensuring proper alignment and stability contributes to the overall performance of machinery, making it a pivotal consideration for anyone involved in mechanical design and maintenance. Understanding the principles behind Bearing Lock is essential for optimizing mechanical systems and ensuring their longevity in demanding operational environments.
What is Bearing Lock and Its Importance in Mechanical Design
Bearing locks play a crucial role in mechanical design by ensuring the
stability and efficiency of rotational components. A bearing lock is essentially a mechanical device that secures bearings onto shafts,
preventing them from shifting or becoming misaligned during operation. This securement is vital, as even the slightest movement can lead to
increased wear and tear, reduced performance, and ultimately, failure of mechanical systems. By providing a robust locking mechanism,
bearing locks contribute significantly to the durability and reliability of machinery.
The importance of bearing locks extends beyond mere functionality; they also enable
designers to optimize the performance of their systems. In applications where high speeds or heavy loads are present, the risks associated
with bearing displacement are amplified. Effective bearing locks can help mitigate these risks, resulting in improved efficiencies and
lower maintenance costs. Additionally, incorporating bearing locks into mechanical designs allows for more compact and lighter structures
since the design can accommodate tighter tolerances without compromising integrity. This not only enhances the overall performance of the
machinery but also contributes to advancements in engineering innovation.
Types of Bearing Locks Used in Industrial Applications
Bearing locks are essential components in industrial settings, providing stability and securing positioning for various machinery parts. There are several types of bearing locks commonly utilized across different applications, each tailored to meet specific requirements in mechanical design and usage.
One widely used type is the set screw lock. This method involves tightening a screw against a shaft, which creates friction and holds the bearing in place. Set screw locks are favored for their simplicity and ease of installation, making them suitable for many general-purpose applications. Another popular option is the tapered lock, which uses wedge-shaped sleeves to increase friction as it is tightened, effectively gripping the shaft. Tapered locks offer a robust solution for high-torque applications, where additional holding power is necessary.
Additionally, the keyway lock system employs a key that fits into a slot on both the shaft and the bearing. This design prevents relative motion between the two parts, providing a secure connection. Keyway locks are particularly beneficial in dynamic environments where vibrations could disrupt the integrity of the assembly. Each of these locking mechanisms plays a critical role in ensuring the performance and longevity of machinery in industrial applications.
How Bearing Locks Contribute to Equipment Performance and Longevity
Bearing locks play a crucial role in enhancing equipment performance and longevity in various mechanical applications. By securely positioning bearings and preventing them from shifting under load, bearing locks maintain the integrity of machinery components. This security is essential in situations with high vibration or heavy loads, where movement can lead to misalignment and premature wear. By providing a stable and reliable interface, bearing locks help ensure that each component operates within its intended specifications, maximizing efficiency and effectiveness.
Furthermore, proper use of bearing locks can significantly reduce maintenance costs and downtime. When bearings are secured appropriately, the risk of failures and breakdowns related to misalignment is minimized, leading to longer operational life for equipment. Regular maintenance routines can focus on other critical areas rather than constantly adjusting or replacing misaligned bearings. As a result, industries benefit from increased productivity and reduced operational interruptions, contributing positively to overall equipment lifecycle management. This focus on performance not only enhances the machinery's reliability but also plays a vital role in optimizing resource allocation and operational sustainability.
What is Bearing Lock and How Does It Work in Mechanical Applications
| Bearing Lock Type |
Functionality |
Common Applications |
Benefits |
| Set Screw Lock |
Holds the bearing in position using a set screw that presses against the shaft. |
Electric motors, conveyor systems |
Easy to install, cost-effective, simple maintenance. |
| Self-Locking Bearing Housing |
Utilizes a tapered bore design to lock onto the shaft without additional components. |
Pumps, fans, industrial machinery |
Prevents shaft slippage, reduced vibration. |
| Expansion Lock |
Expands when the bearing is installed, creating a secure fit. |
Heavy machinery, construction equipment |
Accommodates thermal expansion, reduces wear. |
| Keyless Locking System |
Uses friction between surfaces to create a secure locking mechanism without keys. |
Centrifuges, turbines, precision instruments |
Improved torque transmission, easy adjustment. |
| Collar Lock |
Utilizes an outer collar that secures the bearing in place when tightened. |
Automotive parts, assembly lines |
Reliable fastening, reduces loosening over time. |
Installation and Maintenance Guidelines for Bearing Locks
Bearing locks play a critical role in ensuring the stability and performance of rotating machinery. Proper installation and maintenance of bearing locks are crucial for preventing unintended movement, wear, and ultimately, equipment failure. According to a report by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, approximately 30% of all machinery failures can be attributed to improper installation or maintenance of key components like bearing locks.
During installation, it is essential to ensure that the bearing lock engages correctly with the shaft and housing. Misalignment can lead to premature wear and tear. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear or looseness. Maintenance best practices suggest that bearing locks be cleaned and lubricated periodically to mitigate dirt accumulation and corrosion, which can compromise their effectiveness. The Society of Tribologists and Lubrication Engineers recommends using high-quality lubricants specifically designed for mechanical applications to enhance the lifespan of bearing locks.
To maximize the operational lifespan of bearing locks, adhering to specified torque settings during installation is vital. Over-tightening can lead to distortion and cracking, while under-tightening may not provide sufficient grip. A systematic approach to inspection and maintenance—not exceeding the guidelines provided by the equipment manufacturer—can significantly reduce the risk of mechanical failures and downtime, as highlighted in several industry studies where maintenance programs showed a 25% reduction in equipment failure rates when proper procedures were followed.
Common Applications of Bearing Locks in Various Industries
Bearing locks play a crucial role in various mechanical applications across multiple industries, ensuring stability and functionality in machinery. These locking mechanisms are essential in preventing axial movement and maintaining proper alignment of rotating components. In the automotive sector, for instance, bearing locks are frequently utilized in wheel hubs and transmission systems, where precise positioning is vital for performance and safety. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the automotive bearing market is expected to reach USD 32.5 billion by 2025, driven in part by the increased demand for efficient locking mechanisms that enhance vehicle performance.
In the manufacturing and industrial sectors, bearing locks are central to the operational reliability of equipment such as conveyor systems and heavy machinery. A research article from Technavio indicates that the industrial bearings market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5% through 2024, highlighting the importance of robust bearing solutions in maintaining productivity. Additionally, in renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines, bearing locks ensure the stability of rotating components under varying loads and environmental conditions, thus optimizing energy output. The integration of advanced bearing locks in these settings exemplifies their versatility and critical role in enhancing operational efficiency across different industries.
Common Applications of Bearing Locks in Various Industries

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us