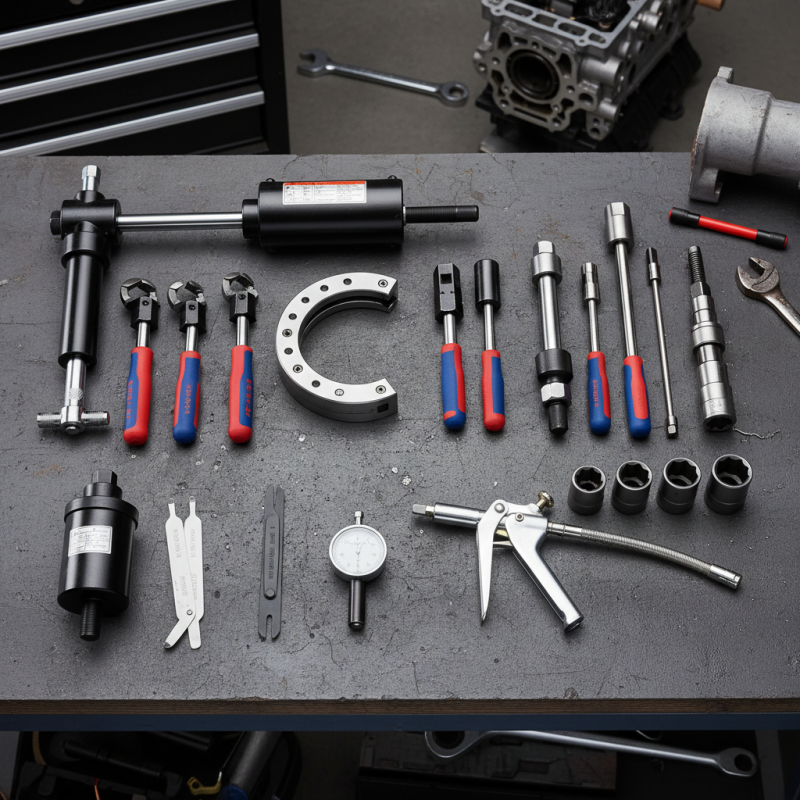
Top 10 Essential Bearing Tools Every Mechanic Should Have
In the world of automotive repair and machinery maintenance, the importance of specialized tools cannot be overstated. Among these, bearing tools play a critical role in ensuring efficient and precise operations. According to a recent report from the Machinery and Equipment Maintenance Industry, approximately 25% of operational downtime in manufacturing settings can be attributed to bearing failures, emphasizing the need for mechanics to be well-equipped with the right tools.
As mechanics strive to enhance their productivity and accuracy, the incorporation of essential bearing tools into their toolkit becomes paramount. These tools not only facilitate the proper installation and removal of bearings but also contribute to extending the lifespan of equipment. Studies indicate that regular maintenance using appropriate bearing tools can reduce replacement costs by up to 40%, making them a vital investment for professionals in the industry.
With advancements in technology, the variety and efficacy of bearing tools have significantly improved, providing mechanics with improved ergonomics and efficiency. This article outlines the top ten essential bearing tools every mechanic should possess, underscoring the indispensable role they play in modern mechanical work.

Essential Bearing Tools: Understanding their Importance in Mechanics
When it comes to mechanics, the importance of essential bearing tools cannot be overstated. Bearings play a pivotal role in the functioning of various machinery, reducing friction and enabling smooth operation. According to a report from the International Bearing Association, over 40% of machinery failures can be traced back to inadequate bearing maintenance and improper installation. Therefore, having the right tools is crucial for ensuring longevity and optimal performance of bearings in any mechanical system.
For instance, a bearing puller is indispensable for safely removing bearings without damaging surrounding components. Similarly, a bearing installation tool aids in maintaining the integrity of the bearing during installation, minimizing the risk of misalignment. Mechanics who invest in these essential tools can reduce repair time and costs significantly; data shows that effective bearing installation can improve machine efficiency by up to 30%.
Tips: Always keep your tools organized and in good condition. Regularly inspect your bearing tools for wear and tear, and replace them as necessary to avoid complications during repairs. Additionally, consider calibrating your tools periodically to ensure they are functioning correctly, which can prevent costly mistakes during bearing work.
The Must-Have Tools for Bearing Installation and Removal
When it comes to bearing installation and removal, having the right tools can significantly enhance efficiency and precision in mechanical work. According to a recent industry report, nearly 70% of mechanical failures are attributed to improper bearing handling and installation. This underscores the importance of possessing essential tools designed specifically for these tasks. A proper bearing puller, for instance, allows for the safe and effective removal of bearings from shafts without causing damage. Similarly, a bearing installation tool ensures that new bearings are fitted correctly, thereby extending their lifespan and improving overall machine performance.
Another crucial tool in the mechanic’s toolkit is the torque wrench, which is vital for applying the correct amount of force during installation. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) emphasizes that accurate torque application can prevent premature bearing failure and enhance equipment reliability. Moreover, a set of calibrated drift pins aids in aligning bearings during installation, further avoiding any potential misalignment that could lead to operational issues. As mechanical tasks evolve, the continuous development of specialized bearing tools remains essential for every professional looking to ensure quality and durability in their work.
Top 10 Essential Bearing Tools Every Mechanic Should Have
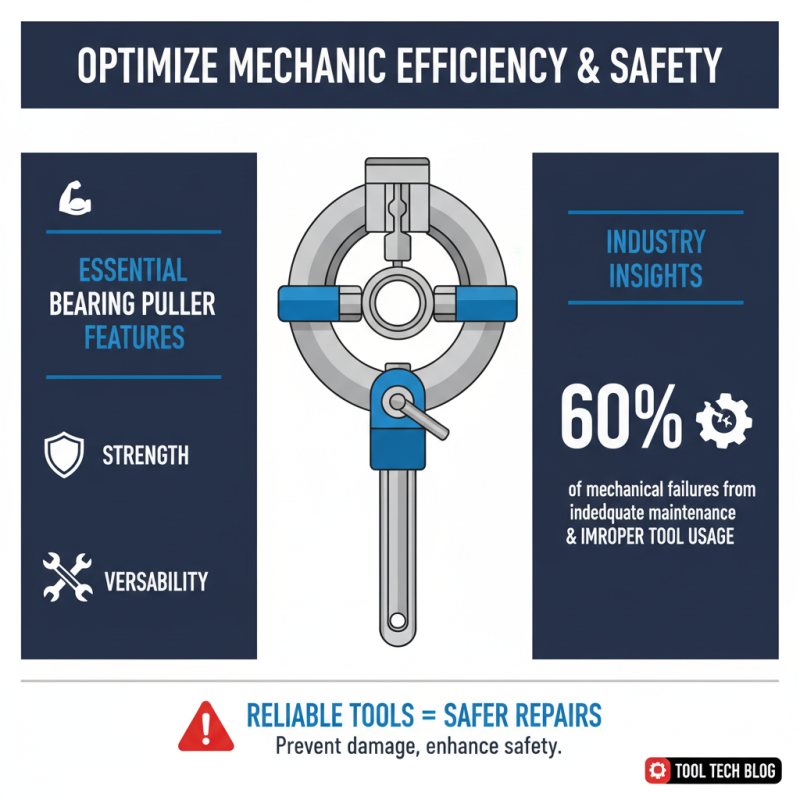
Key Features of Quality Bearing Pullers Every Mechanic Should Know
When it comes to bearing pullers, understanding their essential features can significantly enhance a mechanic's efficiency and safety. A quality bearing puller should exhibit exceptional strength, durability, and versatility. According to recent industry data, more than 60% of mechanical failures in vehicles are attributed to inadequate maintenance and improper tool usage. This underscores the necessity for technicians to utilize reliable and efficient tools, including pullers that can handle the stresses of removing bearings safely without damaging other components.
One of the key features to look for in bearing pullers is their construction material. Tools made from high-grade steel not only provide superior strength but also ensure longevity under strenuous conditions. Furthermore, adjustable arms can be crucial; a puller with flexible or interchangeable arms can accommodate various bearing sizes and types, enhancing a mechanic's ability to tackle different jobs effectively. Additionally, features such as a built-in lock mechanism provide increased safety by preventing accidental slips during operations, which can lead to workplace injuries. Several industry reports indicate that mechanics equipped with high-quality tools experience fewer accidents and improve overall service times by up to 30%. Understanding and investing in these essential features can make a significant difference in a mechanic's daily operations.
Essential Lubrication Tools for Maintaining Bearings Effectively
When maintaining bearings, effective lubrication is crucial to ensure their longevity and optimal performance. One of the essential tools for this task is a high-quality grease gun. This tool allows mechanics to apply lubricants precisely where they are needed, minimizing waste and avoiding contamination. Regular lubrication helps reduce friction and wear, ultimately prolonging the life of the bearings and the machinery they support.
Another important lubrication tool is a bearing oil applicator, which is particularly useful for bearings requiring liquid lubricants. This tool enables a controlled application of oil, ensuring that it reaches all necessary areas without over-saturating. Additionally, using a lubricant reservoir can streamline the process, allowing mechanics to keep different types of lubricants on hand for various applications. This organization enhances efficiency and ensures that the right type of lubricant is always readily available when needed, promoting effective maintenance practices and reducing downtime.
Top 10 Essential Bearing Tools Every Mechanic Should Have - Essential Lubrication Tools for Maintaining Bearings Effectively
| Tool Name |
Description |
Material |
Usage |
Maintenance Frequency |
| Bearing Puller |
Helps to remove bearings from their housings without damage. |
Steel |
Used during bearing replacement. |
As needed |
| Grease Gun |
Applies grease to bearings for lubrication. |
Aluminum or Steel |
Used regularly to maintain bearing lubrication. |
Weekly |
| Bearing Checker |
Tests bearing condition and identifies potential issues. |
Plastic or Steel |
Routine checks during maintenance. |
Monthly |
| Oil Siphon |
Removes old oil or lubricant from bearing housings. |
PVC or Rubber |
Used during lubrication service. |
Before lubrication |
| Torque Wrench |
Ensures proper fastening of bearing components. |
Steel |
Used during installation. |
As needed |
| Cleaning Kit |
Includes brushes and solvents to clean bearings. |
Various |
Used before applying new lubricant. |
As needed |
| Dial Indicator |
Measures bearing runout or misalignment. |
Metal |
Used for precise alignment checks. |
As needed |
| Bearing Installation Tool |
Facilitates safe installation of bearings. |
Aluminum |
Used during bearing installation. |
As needed |
| Digital Caliper |
Measures inner/outer diameter and thickness of bearings. |
Stainless Steel |
Used to select proper bearings. |
As needed |
| Lifting Equipment |
Helps to lift heavy components while working on bearings. |
Steel |
Used for safety during heavy lifting. |
As needed |
Safety Equipment for Bearing Handling and Maintenance by Mechanics
When handling and maintaining bearings, safety should be the top priority for mechanics. According to a report by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, over 400,000 injuries occur each year in workplaces involving machinery, highlighting the critical need for proper safety equipment. Essential safety gear includes gloves, goggles, and steel-toe boots, which protect mechanics from potential hazards such as sharp edges and heavy machinery. Moreover, using ergonomic tools can reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries, a common issue when performing repetitive tasks.
Tips for safely handling bearings include maintaining a clean workspace to minimize the risk of slips and falls, and ensuring that all tools are in good condition before use. Mechanics should also utilize proper lifting techniques when handling heavy components to prevent injuries. It is vital to have a safety data sheet (SDS) available for any lubricants or cleaning agents employed, ensuring that all personnel are informed about handling and emergency procedures.
Furthermore, investing in quality storage solutions for bearing tools and components not only organizes the workspace but also reduces injury risks. Mechanics who follow these guidelines show a commitment to workplace safety, contributing to a more efficient and productive environment. Emphasizing safety equipment in the maintenance of bearing tools is not just best practice—it is essential for the well-being of all involved.

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us