How to Optimize Bearing Design for Maximum Efficiency and Performance
In the realm of engineering, optimizing bearing design is crucial for enhancing mechanical systems' efficiency and performance. As noted by Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in the field of bearing technology, "The intricacies of bearing design can significantly influence the overall durability and effectiveness of machinery." This underscores the importance of a meticulous approach to bearing design, where even minor modifications can yield substantial improvements.
Bearing design is not merely about functionality; it encompasses a comprehensive understanding of material properties, load distribution, and lubrication methods. By incorporating advanced computational techniques and innovative materials, engineers can refine bearing designs to meet the demanding requirements of modern applications. The pursuit of optimization in bearing design can lead to reduced friction, greater lifespan, and enhanced reliability in various mechanical systems, ultimately contributing to increased productivity and efficiency.
As industries evolve and push the boundaries of technology, the significance of optimizing bearing design becomes even more pronounced. Engineers and designers must keep abreast of the latest advancements and best practices to ensure that their bearings not only meet current demands but also anticipate future challenges in performance and sustainability.

Understanding the Basics of Bearing Design and Functionality
Bearing design is a critical aspect of mechanical engineering that directly impacts the performance and longevity of machinery. At its core, a bearing serves to reduce friction between moving parts, allowing for smoother operations and greater efficiency. The basic functionality of a bearing revolves around supporting loads while enabling rotational or linear movement. Understanding the geometry, materials, and lubrication methods used in bearing design is essential for optimizing efficiency and ensuring reliable performance.
The shape and size of bearings vary greatly depending on their application. For instance, rolling element bearings, such as ball and roller bearings, are designed to handle radial and axial loads with minimal friction. The choice of materials, like high-strength steel or ceramic, can significantly influence a bearing's durability and operational efficiency. Furthermore, the implementation of effective lubrication systems helps to minimize wear and tear, extending the bearing's lifespan. Overall, a solid grasp of these fundamental aspects of bearing design facilitates the creation of systems that operate at peak efficiency, minimizing energy consumption while maximizing performance.
How to Optimize Bearing Design for Maximum Efficiency and Performance
| Bearing Type |
Load Rating (kN) |
Speed Limit (RPM) |
Material |
Cost ($) |
| Radial Ball Bearing |
15.0 |
12000 |
Steel |
20 |
| Thrust Roller Bearing |
25.0 |
6000 |
Carbon Steel |
45 |
| Angular Contact Bearing |
20.0 |
15000 |
Chrome Steel |
30 |
| Spherical Roller Bearing |
35.0 |
8000 |
Alloy Steel |
60 |
| Deep Groove Bearing |
10.0 |
20000 |
Stainless Steel |
25 |
Identifying Key Factors Influencing Bearing Efficiency
Bearing efficiency is critical for enhancing the performance of various mechanical systems. Several key factors influence bearing efficiency, including lubrication quality, material selection, and load conditions. According to a report by the American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA), improper lubrication can reduce bearing life by up to 60%, making the choice of lubricant crucial for maximizing operational efficiency. High-quality lubricants minimize friction, which, according to a study published in the Journal of Tribology, can improve efficiency by approximately 15%, allowing machinery to operate smoother and last longer.
Material selection also plays a significant role in bearing performance. Advanced materials like ceramic and hybrid composites exhibit lower friction coefficients and higher wear resistance compared to traditional steel bearings. A study by the University of Michigan highlights that bearings made from advanced materials can withstand higher loads and temperatures, leading to a significant increase in both performance and efficiency. Environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and contamination must also be considered, as they can drastically affect bearing operation. Implementing effective sealing solutions can reduce the ingress of contaminants, further enhancing the operational efficiency of bearings in demanding applications.
Optimizing Bearing Design for Maximum Efficiency
This chart illustrates the key factors influencing bearing efficiency, showcasing how improvements in each factor can lead to enhanced performance in bearing applications.
Selecting Materials for Enhanced Bearing Performance
Selecting the right materials for bearing design is critical in optimizing performance and efficiency. The selection process should consider parameters such as load capacity, wear resistance, and operating temperature. According to a report by the American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA), the choice of materials can significantly impact bearing life and operational reliability. For instance, high-quality steel alloys and advanced composites can enhance durability and reduce friction, resulting in improved energy efficiency.
Tips: When selecting materials, prioritize those that offer a combination of high strength and low weight, like titanium or certain plastics, to reduce energy consumption and improve performance.
Moreover, surface treatments and coatings play a vital role in maximizing bearing effectiveness. Implementing processes like nitriding or applying ceramic coatings can enhance the surface hardness and reduce wear rates, according to a study published in the Journal of Engineering Tribology. These treatments can improve the fatigue life of bearings under high-load conditions significantly.
Tips: Consider utilizing tribological performance testing for different coating options to identify the best match for specific operational conditions, ensuring optimal performance under varying loads and speeds.
Implementing Advanced Design Techniques for Optimization
Implementing advanced design techniques is crucial for optimizing bearing performance and efficiency. One of the most effective approaches involves the use of computer-aided design (CAD) software, which enables engineers to create detailed models of bearing systems. With this technology, designers can simulate various operating conditions and stress factors, allowing them to identify potential weaknesses or inefficiencies in the initial design. The ability to visualize and manipulate components in a virtual environment aids in making informed decisions about material selection and geometric configurations.
Another technique is the integration of finite element analysis (FEA), which provides insights into how bearings respond under different loads and rotational speeds. By applying this method, designers can refine the geometry of the bearing, enhancing its load distribution characteristics and minimizing points of failure. Additionally, using advanced materials with superior wear resistance and low friction properties can significantly improve the bearing's overall performance. By leveraging these design techniques, engineers can develop bearings that not only function more efficiently but also have extended service lives, ultimately leading to better performance in various applications.
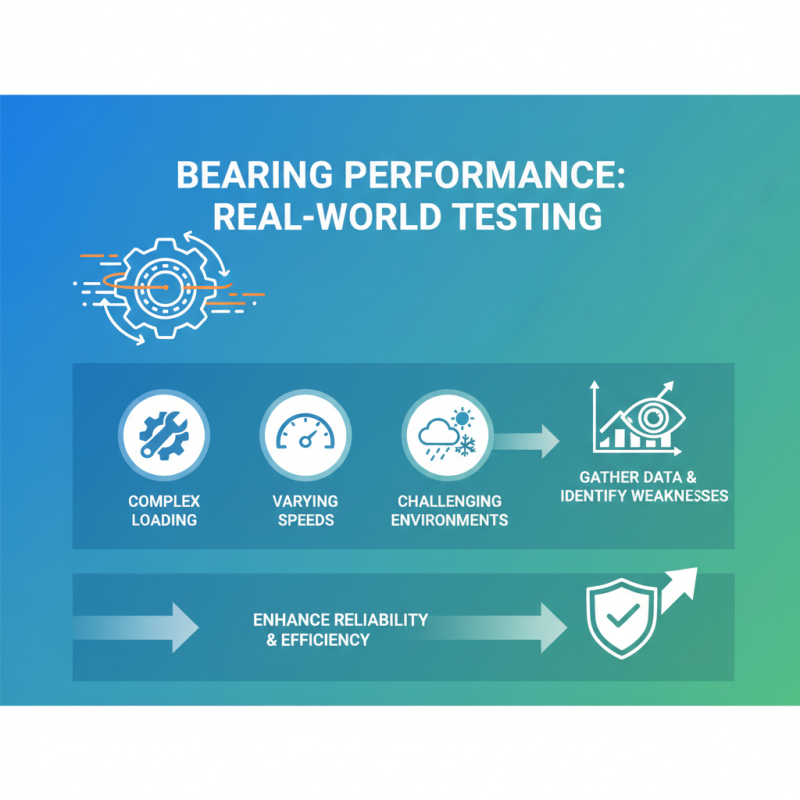
Testing and Evaluating Bearing Performance in Real-World Applications
Testing and evaluating bearing performance in real-world applications is crucial for ensuring that designs meet the necessary efficiency and reliability standards. In practical settings, bearings encounter complex loading conditions, varying speeds, and challenging environmental factors that can significantly impact their operation. Conducting comprehensive tests in environments that simulate these conditions allows engineers to gather valuable data on how bearings perform over time. This information is essential for identifying weaknesses in design and for making informed adjustments to enhance reliability and efficiency.
Real-world testing methods, such as fatigue testing, temperature monitoring, and lubricity assessments, provide insights into bearing behavior under stress. These assessments enable engineers to evaluate critical performance indicators, including wear resistance, friction levels, and heat generation. In addition, using advanced measurement techniques such as vibration analysis and acoustic emission monitoring can uncover potential issues before they lead to premature failure. Collectively, these evaluations are fundamental in optimizing bearing design, ensuring that each component functions effectively while maximizing overall system performance.

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us