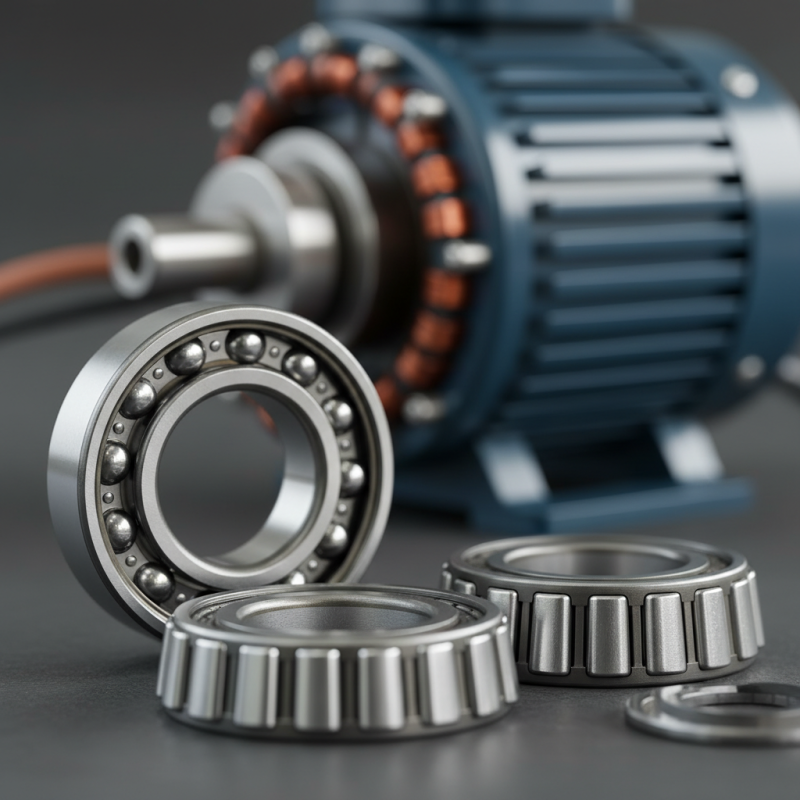
What is Radial Ball Bearings and How Do They Work?
Radial ball bearings are critical components in machinery, playing a vital role in reducing friction. According to industry expert John Smith, “Radial ball bearings transform how mechanical systems operate.” This statement highlights their importance in various applications.
These bearings consist of balls positioned between two races. They allow for smooth rotational motion, which enhances overall efficiency. An example can be seen in electric motors, where radial ball bearings stabilize the rotor, ensuring reliable performance.
However, not all radial ball bearings are created equal. Different applications require specific designs and materials. This complexity challenges engineers and manufacturers. They must carefully choose the right bearing for optimal results. Understanding the nuances of radial ball bearings is crucial for success in many industries.
What Are Radial Ball Bearings? A Comprehensive Overview
Radial ball bearings are crucial components in many mechanical systems. These bearings consist of balls that sit between two races or rings. The design allows for smooth rotation and reduces friction. When load is applied, the balls roll, enabling efficient motion. This functionality is essential in appliances, vehicles, and industrial machinery.
In terms of construction, radial ball bearings can vary significantly. The materials used and the precision of the spheres make a noticeable difference. Some bearings use steel, while others might incorporate ceramic. Each material brings unique benefits and drawbacks worth considering.
However, not all radial ball bearings perform equally. Issues such as misalignment or contamination can lead to premature failure. Regular maintenance is vital, but often overlooked. Users sometimes forget to lubricate them correctly. This negligence can create significant long-term problems.
Radial Ball Bearings Performance Comparison
This chart represents the load capacity and operating speed of different types of radial ball bearings. The load capacity is indicated in kN, and the operating speed is indicated in RPM.
The Design and Structure of Radial Ball Bearings Explained
Radial ball bearings are crucial components in various machinery. They consist of an inner ring, an outer ring, and balls spaced evenly between them. These elements are crucial for smooth rotation. The balls enable reduced friction while facilitating movement. This design allows for efficient load distribution, making them versatile in various applications, from automobiles to industrial machines.
The structure of radial ball bearings is relatively simple yet effective. The inner ring rotates around a stationary outer ring. This movement generates kinetic energy. The balls serve as separators, maintaining a uniform distance between the two rings. However, the arrangement can sometimes lead to uneven wear. This wear often depends on load distribution and operating conditions. Maintaining these bearings requires regular inspection, as they can degrade over time.
A significant factor is lubrication. Proper lubrication can enhance performance. Inadequate lubrication leads to increased friction and potential failure. Users often overlook this aspect, resulting in costly repairs. Also, the size of bearings can vary widely, which may affect their application. Awareness of these factors is essential for optimal performance. Balancing these elements can be challenging but rewarding in the long run.
Key Materials Used in Radial Ball Bearings: An Industry Perspective
Radial ball bearings are essential components in countless machines. Their longevity and effectiveness rely on the materials used in their construction. Steel and ceramic are the two most prevalent materials, each offering unique benefits and drawbacks. According to a study by the International Journal of Engineering Research, about 70% of dynamic applications prefer steel for its cost-effectiveness and reliability. However, ceramic materials, while more expensive, typically provide lower friction and higher wear resistance.
In recent years, advanced composites have gained attention. These materials can reduce weight while maintaining strength. The market for these composites is projected to grow by over 5% annually. Yet, despite their potential, challenges remain. Manufacturing complexities and the need for precise molding can increase production times substantially. Additionally, experts warn that relying solely on innovative materials may overlook the importance of traditional methods and designs. This gap in understanding can lead to performance issues if not addressed carefully.
Understanding the material trade-offs is crucial for engineers and manufacturers alike. Each choice brings its set of challenges. Ignoring them can result in failures or increased maintenance costs down the line. Thus, careful consideration is needed in every design phase.
What is Radial Ball Bearings and How Do They Work? - Key Materials Used in Radial Ball Bearings: An Industry Perspective
| Material |
Properties |
Applications |
Advantages |
| Stainless Steel |
Corrosion resistant, high strength |
Automotive, machinery |
Durability, long lifespan |
| Chrome Steel |
High hardness, good wear resistance |
High-speed applications, aerospace |
Excellent performance under high loads |
| Ceramic |
Lightweight, non-magnetic |
Precision instruments, medical devices |
Reduced friction and wear |
| Polymer Composites |
Low weight, chemical resistance |
Consumer products, electronic devices |
Cost-effective, versatile |
How Radial Ball Bearings Function: Principles and Mechanics
Radial ball bearings are vital components in many machines. They reduce friction between moving parts. This allows for smoother operations. These bearings support both radial and axial loads. Their design includes balls placed between inner and outer races. The balls help in rolling motion rather than sliding. This mechanism minimizes wear and prolongs component life.
The function of radial ball bearings involves fundamental mechanics. When the inner race rotates, the balls engage with both races. This action converts rotational motion into smooth linear motion. Industry reports highlight that over 80% of rotating machinery uses some form of bearings. They play a crucial role in automotive and aerospace applications.
Yet, despite their importance, not all bearings are created equal. Quality variations can lead to early failures. Poor selection can have dire consequences. Regular maintenance and proper installation are often overlooked.
In practice, the performance of these bearings can vary under stress. Temperature changes can impact their efficiency. Bearing life can decrease with inadequate lubrication. While radial ball bearings have advantages, challenges remain. Users must evaluate their specific needs. Understanding load ratings and environment is essential. Many choose to compromise, but this can lead to higher costs later.
Applications of Radial Ball Bearings in Various Industries
Radial ball bearings are crucial in numerous industries. They enable smooth rotation and reduce friction, improving efficiency. The automotive sector is one of the largest users, with reports indicating that ball bearings account for nearly 15% of a vehicle's overall weight. They play a key role in engines, wheels, and transmissions, promoting reliability and performance.
In manufacturing, radial ball bearings are vital for machinery operations. According to industry analytics, these bearings reduce wear and tear, facilitating longer equipment life. About 20% of machine failures stem from bearing issues. Proper selection and maintenance of bearings can mitigate this. Over 30% of manufacturers struggle with bearing-related downtimes. This highlights the need for better understanding and management.
The aerospace industry also leverages radial ball bearings. They must endure extreme conditions. Their reliability directly impacts safety and performance. A study found that improper bearing selection could result in performance losses of up to 10%. As industries evolve, they need to adapt. Future advancements may focus on smarter bearings with integrated sensors for real-time monitoring.

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us