Top 10 Steel Bearings Types You Should Know?
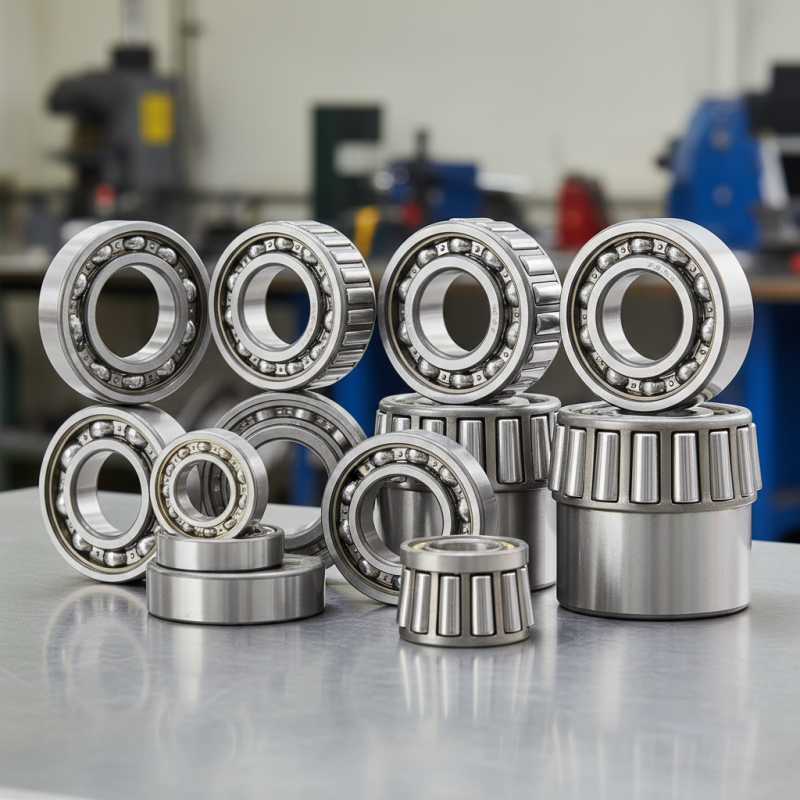
Steel bearings play a vital role in modern machinery and equipment. They are essential for reducing friction and enhancing performance. Different types of steel bearings cater to various applications. Understanding these types can help optimize functionality.
When exploring steel bearings, one must consider factors like load capacity, speed, and environment. Each type serves unique purposes. For instance, some are designed for high-speed applications, while others excel under heavy loads. This spectrum of options can be overwhelming. The wrong choice may lead to reduced efficiency or even equipment failure.
In this article, we dive into the top 10 steel bearings types. Each type is dissected, highlighting features, benefits, and ideal applications. By the end, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about your needs. Steel bearings are not merely components; they are crucial to seamless operation in various industries.
Types of Steel Bearings: A Comprehensive Overview
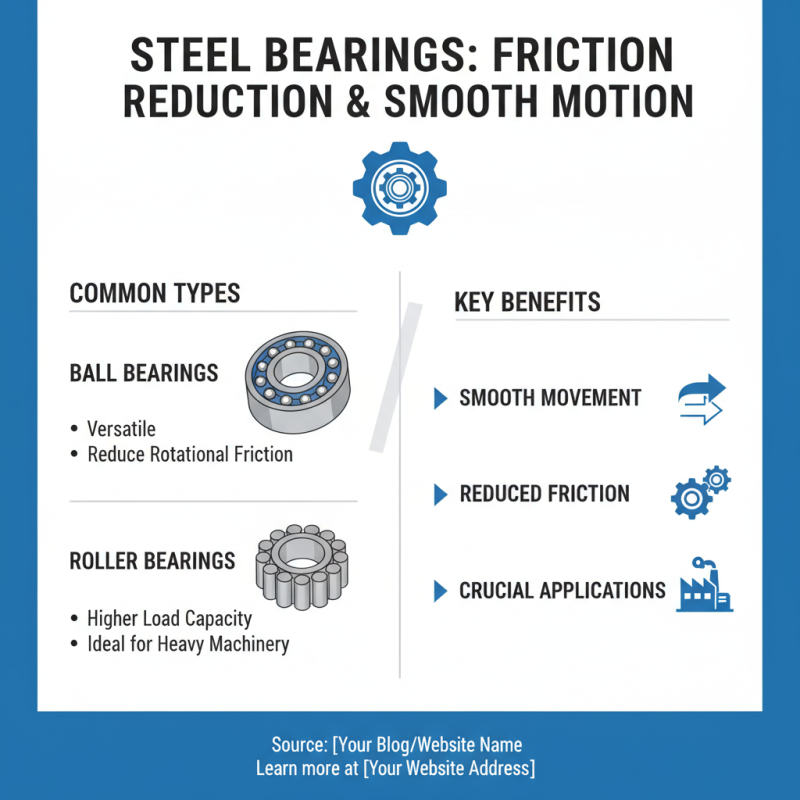
Steel bearings play a crucial role in various applications. They ensure smooth movement and reduce friction. There are different types of steel bearings, each designed for specific tasks. Ball bearings are commonly used for their versatility. They consist of balls that reduce rotational friction. In contrast, roller bearings have cylindrical elements, offering a higher load capacity. This makes them ideal for heavy machinery.
Thrust bearings focus on axial loads, allowing them to handle pushing forces. They are essential in applications like gearboxes. Needle bearings are another type. They have long, thin rollers that save space while supporting heavy loads. However, their design can lead to excessive wear if not maintained properly. The importance of regular inspection cannot be overstated.
Some bearings are better suited for high-speed applications. Ceramic hybrid bearings, for example, offer enhanced performance. Yet, they are often more expensive and may not suit all budgets. Each type has its advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these nuances helps in making informed choices. Ideally, one should evaluate the specific needs before selecting the right bearing type. This careful consideration can lead to improved efficiency and longevity.
The Functionality of Different Steel Bearings in Machinery
Steel bearings play a crucial role in machinery. They reduce friction, facilitate smooth rotations, and improve overall efficiency. Different types serve various functions, impacting performance significantly. According to a recent industry report, more than 60% of machinery failures are linked to bearing damage. This highlights their importance in operational reliability.
Ball bearings, for example, are widely used for their versatility. They handle radial and axial loads, which makes them ideal for motors and gearboxes. Roller bearings, on the other hand, are better suited for heavy loads. Their design provides increased contact area. However, they can be less efficient at high speeds. It's essential to choose the right type based on specific application needs.
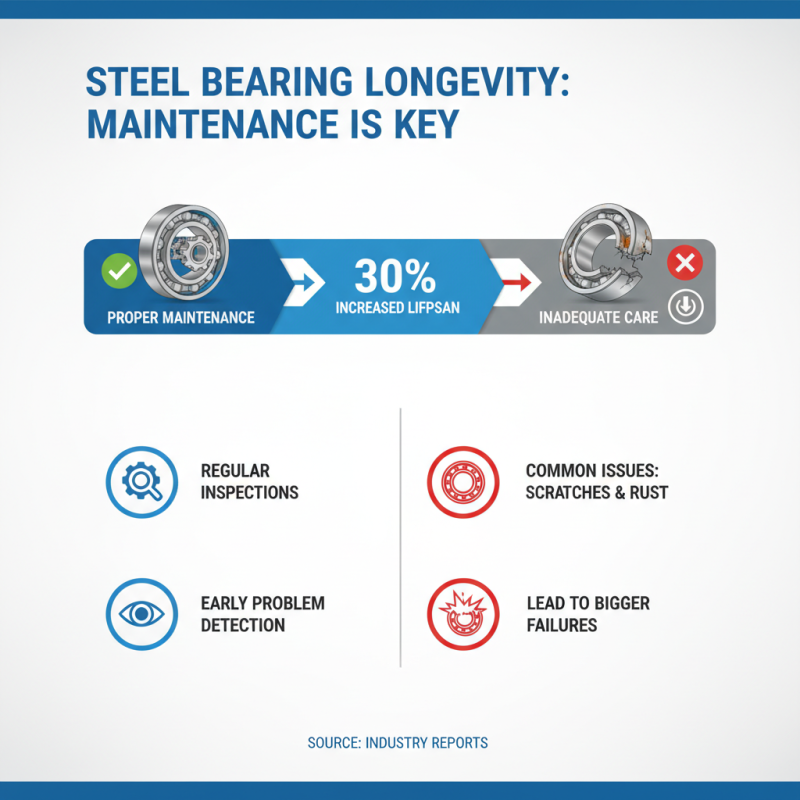
Additionally, the material quality plays a significant role in bearing performance. High-carbon chromium steel is preferred for its durability. Yet, some manufacturers compromise on this, leading to premature failures. Regular maintenance of bearings is often overlooked. The industry's best practices suggest that 30% of machinery downtime could be avoided with proper care. This reflects a critical area for improvement in operational efficiency.
Top 10 Steel Bearings Types You Should Know
| Bearing Type |
Material |
Load Capacity (kg) |
Speed (RPM) |
Application |
| Deep Groove Ball Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
3500 |
18000 |
Electric Motors |
| Angular Contact Ball Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
4000 |
15000 |
Machine Tool Spindles |
| Self-Aligning Ball Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
3000 |
12000 |
Conveyor Systems |
| Tapered Roller Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
7000 |
12000 |
Automotive Applications |
| Spherical Roller Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
8000 |
8000 |
Heavy Machinery |
| Needle Roller Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
2500 |
20000 |
Compact Spaces |
| Thrust Ball Bearing |
Chrome Steel |
2000 |
8000 |
Rotary Applications |
| Plain Bearing |
Bronze |
4000 |
Varies |
General Machinery |
| Magnetic Bearing |
Electromagnetic Materials |
Unlimited |
Varies |
High-Speed Applications |
| Fluid Bearing |
Lubricating Fluid |
Varies |
Varies |
Pumps & Compressors |
Comparative Analysis of Ball Bearings and Roller Bearings
When comparing ball bearings and roller bearings, several key differences emerge.
Ball bearings consist of smooth balls that roll. They are great for applications requiring low friction.
Roller bearings, on the other hand, use cylindrical rollers. These provide a larger contact area, which helps with heavy loads.
Ball bearings work well in high-speed environments. However, they can wear out faster under heavy loads. This is a crucial limitation. In contrast, roller bearings excel in supporting heavy items. They can handle shock loads better. Yet, they often produce more friction at high speeds. The choice depends on specific application needs, which can be complex and nuanced.
In real applications, anticipating failures is sometimes challenging. Users may underestimate load capacities. On some occasions, improper lubrication leads to premature wear. Identifying the right type for your needs is not straightforward. Each type has its own quirks and best-use scenarios. Therefore, understanding these differences becomes essential for effective maintenance and longevity.
Applications of Various Steel Bearings in Industries
Steel bearings play a crucial role in various industries. They provide support, reduce friction, and enhance machinery performance. According to recent reports, the global bearing market is expected to reach $139 billion by 2026. This growth indicates a rising demand for efficient components that can withstand harsh conditions.
In the automotive sector, steel bearings are indispensable. They are used in engines, transmissions, and wheel hubs. The automotive sector accounts for over 40% of the bearing market. Their reliability directly impacts vehicle safety and performance. However, the increasing complexity of automotive designs means that common bearings may not always meet the needed specifications.
Manufacturing and machinery also heavily rely on steel bearings. They ensure smooth operation in conveyor systems and CNC machines. A study revealed that improper bearing selection can lead to 30% increased downtime. This inefficiency highlights the need for precise engineering and selection of bearing types. Industries must prioritize sustainability and lifecycle costs when choosing bearings for their equipment and machinery.
Maintenance and Care Tips for Steel Bearings Longevity
When it comes to steel bearings, proper maintenance is crucial for their longevity. According to industry reports, inadequate care can reduce bearing lifespan by up to 30%. Regular inspections help in identifying potential issues early. A small scratch or rust can lead to bigger problems later.
Lubrication is key. Ensure that the bearings are well-lubricated using the right type of grease. Over-lubrication can attract dirt, while under-lubrication leads to friction. Both scenarios are detrimental. Aim for consistency in lubrication intervals, typically every 500 hours of operation or as recommended.
Keep the operating environment clean. Contaminants can easily damage bearings. Regularly clear debris and monitor for moisture. Even small amounts of water can cause corrosion. Remember, a clean workspace often results in better bearing performance. Regular checks and a vigilant approach to maintenance can save costs in the long run.

Home
Products
Industrial Bearings
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Self-Aligning Ball Bearings
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Taper Roller Bearings
Spherical Roller Bearings
Bearing housing or Accessories
Miniature Bearing
Thrust ball bearing
Radial Spherical Plain Bearing
Pillow Block Bearing
Needle Roller Bearings
Automotive Bearings
Agricultural Bearings
Special Material Bearings
Industry Application
About Us
News
Contact Us